Carpal Tunnel Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide to Early Signs & Stages

Wrist pain is unnerving for all but ‘Is it carpal tunnel symptoms?’ This is a common query we get, especially from manual workers, middle-aged & older adults, gamers and pregnant women. Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects about 3% of the Canadian population. Mild to moderate occasional numbness is among the early symptoms. While people tend to ignore the symptoms initially, diagnosing and treating the problem from an early stage can help prevent further problems like surgery. This blog discusses all the symptoms of CTS so you can self-identify and talk to your medical professional accordingly.
What are the Early Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
CTS is a progressive disorder. That means it can get worse with time. The best way to handle wrist or finger pain is to notice the symptoms at an early stage and consult a physiotherapist right away. Physiotherapists or physical therapists are trained in treating mild to moderate CTS symptoms, and the chances of surgery can also be minimized.
Tingling sensations– Most patients report a tingling/numbness sensation in the fingers and hands. However, the numbness may not show up all the time. They come and go like episodes, often during sleep or occupational tasks.
Nocturnal paresthesia– Patients frequently report that their carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms at night are more profound. The feeling is uncomfortable enough to wake you from sleep. This is called nocturnal paresthesia in the context of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and is one of the most important biomarkers for confirming CTS.
Morning fumble– Some people may find their hands feel stiff, swollen and clumsy for about 15-20 minutes after waking up. You may struggle with simple tasks like holding a toothbrush or turning a doorknob.
Numbness boundary– In the early stages, the tingling sensation is limited to 3.5 fingers- thumb, index, middle and half of your ring finger. The side of the ring finger by the little finger feels normal. The sensations are usually not present there in the early stages.
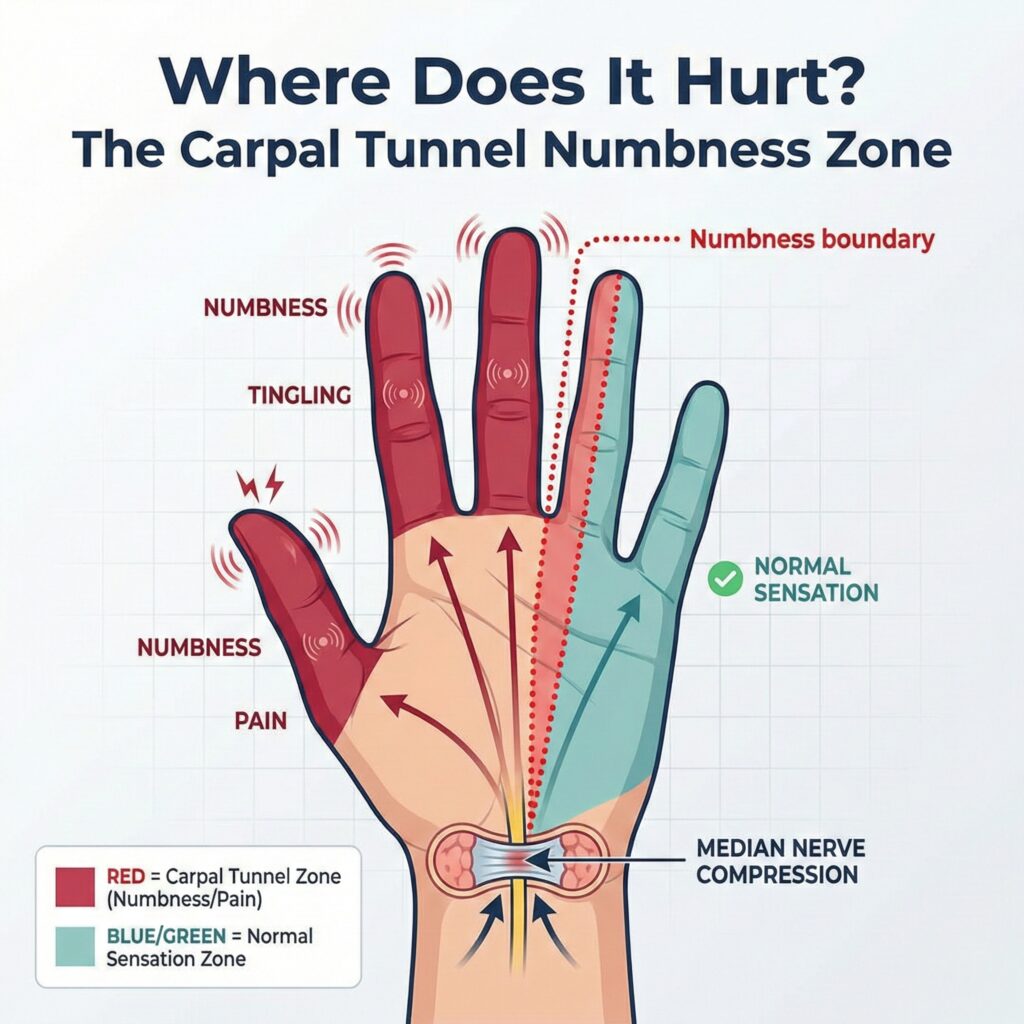
Functional deficit- A loss of very basic functional strength is also an early indicator of CTS. You may tend to drop small objects like pens or keys. This can be confused with a simple weakness in muscle strength. But it is better to get the wrist checked to rule out CTS medically.
Listen to your body because it sends signals when something is wrong with it inside. The tingling/numbness sensations are very common. If you experience it or feel loss of strength in the wrists, go to your nearest physiotherapist and get a proper diagnosis without letting the condition worsen.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel in the Elbow
In the later stages of CTS, the numbness sensations can radiate up to the elbows. Some may also experience elbow pain along with tingling in the fingers. But there are other conditions as well that can cause similar symptoms to CTS. So, a diagnosis is needed to confirm whether it’s carpal tunnel syndrome or any other condition.
The pain can also start at the wrist and reach the shoulders if left untreated. So, patients can get confused whether it’s carpal tunnel symptoms in the shoulders or something else. Yes, it can be some other health condition, depending on where the pain starts.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel in Pregnancy
The chances of carpal tunnel syndrome increase in pregnant women. During pregnancy, the body’s fluid retention capacity increases, causing fluids to build up in various parts of the body, including the wrist. This buildup increases swelling in the ligaments forming the root of your carpal tunnel, which in turn compresses the median nerve passing through the tunnel.
The condition is most likely to show up in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
What are the Other Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Functional symptoms typically appear late in CTS. You may feel a slight weakness in your hands or wrists initially, leading to a deeper level of motor skill compromise.
Patients often report a reduction in grip strength, which makes it difficult for them to perform simple tasks such as opening jars or holding heavy objects. They also show loss of pinch strength since the condition compromises the precision between the thumb and index finger, which otherwise would have been a simple task.
In chronic severe CTS, the muscular bulge at the thumb’s base forms a visible bulge. The thumb loses its normal flexibility, causing the ‘ape’s hand deformity’.
How Do CTS Symptoms Progress?
The symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome progress gradually from mild and moderate to severe and permanent. Here is a glimpse into a typical clinical staging of carpal tunnel syndrome.
| Stage | Frequency of Symptoms | Functional Impact |
| Stage 1: Mild | Intermittent | Minimal. The patient may use the “Flick Sign” to relieve morning stiffness. Sleep is occasionally disturbed. |
| Stage 2: Moderate | Frequent / Persistent | Moderate. Sleep is regularly disturbed. “Clumsiness” begins: difficulty with fine tasks like buttoning. |
| Stage 3: Severe | Constant | Severe. Frequent dropping of objects. Difficulty with basic ADLs. Risk of permanent damage. |
| Stage 4: Advanced | Permanent | Permanent disability. Surgery may prevent worsening, but full recovery is unlikely. |
What Causes the Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The compression of the median nerve (present in the wrist) is the main cause of carpal tunnel syndrome. The compression can occur due to an injury or a fracture. Underlying conditions like diabetes or arthritis can also cause inflammation in the wrists, leading to the compression of the median nerve.
Occupational Factors that Contribute to CTS
Occupational factors are the most significant contributors to work-related CTS. Here are the scenarios where the risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome increase considerably.
Repetitive motion- Performing the same hand or wrist motions repeatedly over long periods of time.
Forceful exertion- Requiring strong gripping, heavy lifting or pinching strength.
Awkward postures- Frequently working with the wrist bent rather than keeping it straight.
Vibration- Prolonged use of vibrating hand-held tools.
Mechanical contact stress– Acquiring direct external pressure on the base of the hand.
| Risk Level | Common Occupations | Primary Stressors |
| Very High | Meat/Poultry/Fish Packing | Cold + High Repetition + Forceful Grip |
| High | Assembly Line Work | High Repetition + Awkward Posture |
| High | Construction / Carpentry | Vibration + High Force |
| Moderate | Sewing / Tailoring | Precision Pinching + Repetition |
| Moderate | Cleaning / Janitorial | Forceful Scrubbing + Posture |
| Variable | Office / Computer Work | Posture (poor ergonomics) + Contact Stress |
How to Alleviate Carpal Tunnel Symptoms?
Here are the simple ways you can manage carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms:
Take rest– Get enough rest to calm down nerves, ensure blood flows smoothly and reduce the inflammation.
Apply cold therapy– Applying an ice pack to the affected wrist for 10-15 minutes can reduce the swelling, causing temporary relief.
Wear the right brace– You may need to wear a splint or brace to protect your wrists from awkward postures, especially during sleep.
Do the right exercises– You can perform gentle exercises to help the median nerve slide through the carpal tunnel freely.
Change specific activities- You may have to identify and change the activities that cause the flare-up of CTS.
Talk to your physiotherapist or doctor when you notice the first symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. They can guide you through the right treatments that can manage the condition and help you get back to a functional life.
When to Get Help?
You should seek medical attention as soon as you notice the initial symptoms, like tinging in the fingers or numbness in the hands. A physiotherapist is trained to treat mild and moderate cases of carpal tunnel syndrome. They diagnose the problem through specific tests to confirm that the condition is indeed CTS. Early detection leads to early diagnosis, followed by a smooth recovery and rehabilitation journey. Whether you experience carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms in both hands or in the fingers, get help quickly to prevent further damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How to relieve carpal tunnel symptoms at night?
You can wear a splint or brace to relieve carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms at night. The brace keeps the wrist in a neutral, straight position. This prevents the median nerve from being compressed while you sleep. Before using any product, consult with a physiotherapist to know if that’s the right thing to do for your pain.
2. Which symptom is typically noticed first in carpal tunnel syndrome?
Typically, the first symptoms in CTS you may notice are the tingling sensations (feels like pins and needles pricking the skin) in the thumb, index and middle fingers. The symptoms come temporarily and go after you shake out your hands for relief.
3. How long do carpal tunnel symptoms last after surgery?
The recovery stage differs from person to person depending on various factors. Typically, tingling sensations or pain at night disappear first within a few days. Other problems, such as incision soreness, fade within weeks or even months. Grip strength can take about 6 to 12 months to recover completely.
Blog Categories
- Acupuncture Treatment (10)
- Ankle Sprain (1)
- Arthritis Treatment (1)
- Back Pain (23)
- carpal tunnel (1)
- Chiropractic Care (39)
- Tennis Elbow (1)
- Chronic Pain (7)
- COVID-19 (1)
- Custom Orthotics (6)
- Dizziness (4)
- Exercises (13)
- Foot Orthotics (6)
- Hamstring Stretches (2)
- Info Articles (3)
- Kids Injury (1)
- Laser Therapy (4)
- Massage Therapy (21)
- Neck Pain (17)
- Orthopedic (1)
- Osteoarthritis (5)
- Osteopathy (3)
- Pain Management (21)
- Physiotherapy Benefits (44)
- Physiotherapy Clinic (6)
- Physiotherapy Exercises (12)
- Physiotherapy Tips (25)
- Physiotherapy Treatment (101)
- Rotator Cuff (2)
- Shin Splints (1)
- Shoulder (2)
- Spine (4)
- Sports Physiotherapy (2)
- Uncategorized (1)
- Vestibular Physiotherapy (2)
- Work From Home (2)



